The Industrial Metaverse: What It Is and How It May Impact Manufacturing
One of the biggest buzzwords in 2021 was “metaverse.” But now, as we approach the end of 2023, this term is nearly absent from the lexicon. What happened to the metaverse and all the exciting innovations set to accompany it? Will we ever experience the potential of the industrial metaverse as the next frontier of manufacturing?
Understanding the industrial metaverse
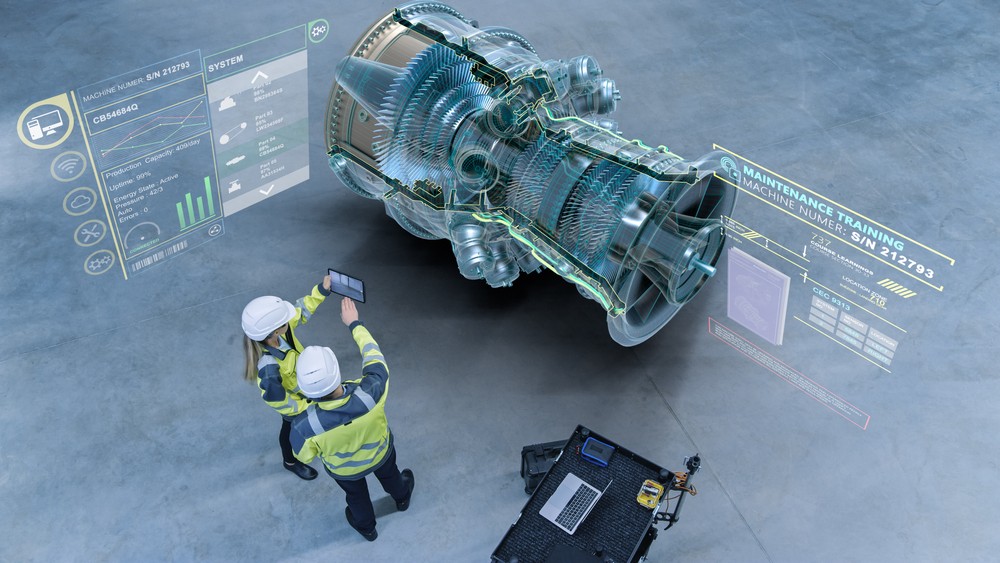
The industrial metaverse combines the physical world with the virtual world. It’s largely powered by technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and digital twins, which create immersive and interactive experiences for industrial applications.
The goal of the industrial metaverse is to improve efficiency, productivity, and safety in industrial settings by providing workers with real-time data and insights, enabling remote collaboration, and creating virtual training environments.

Manufacturing’s last digital frontier
While the technologies designed to power the industrial metaverse have gained traction over the past couple of years, the metaverse itself has yet to unify. Most companies don’t have interconnected ecosystems to bridge real-world operations with digitized counterparts. Instead, there’s a growing collection of use cases building a foundation for such an ecosystem in the future:
- Product design and engineering: Digital twins can create virtual prototypes of products and test them under different conditions before they are built in the real world. This can help to identify and fix design flaws early, saving time and money.
- Manufacturing processes: Virtual reality can be used to train workers on new manufacturing processes and equipment, while augmented reality can provide real-time guidance and instructions during production. The results are improved quality and fewer errors.
- Field service: Augmented reality can provide remote technicians with a real-time view of the equipment they are servicing and guide them through complex procedures, reducing downtime and improving customer satisfaction.

Industrial metaverse use cases
The industrial metaverse remains in its early stages of development. According to a report by the Manufacturing Leadership Council and Deloitte, 92% of manufacturing executives say they are experimenting with or implementing at least one metaverse-related use case.
While not yet manifest, the industrial metaverse is far from a failure to launch. More companies are beginning to align their growing number of use cases around a unified digital approach to manufacturing oversight. Companies leading the way in shaping a more robust industrial metaverse include Siemens, Boeing, and General Electric (GE). Siemens is using digital twins to create virtual factories that optimize production, while Boeing is employing augmented reality to train workers on new aircraft assembly processes. GE is utilizing digital twins to monitor and maintain wind turbines remotely.
As these companies and others invest in digital manufacturing technologies, the metaverse will continue to evolve. New applications are constantly emerging. As the technology matures, it is expected to impact a wide range of industries, making it easier to envision a future of dark factories and wholly automated production with physical systems managed within the industrial metaverse.
