5 Reasons Your Electric Motors Keep Overheating

An overheated electric motor will bring your equipment to a screeching halt. And while excessive heat may be the problem confronting you, knowing how and why your motor overheated is imperative. Until you get to the root of the problem, your motor will continue to reach peak temperatures, failing again and again.
Qualifying an overheated electric motor
The first step in dealing with an overheated motor is to make sure overheating is actually the problem. Unless you’re actively monitoring it when it fails, you may not suspect heat. To verify overheating, you’ll need to get the motor up and running again — this time with methods of monitoring it:
- Check the thermal reset button on your motor if it’s equipped with one. This is the quickest, easiest way to qualify an overheat.
- A simple thermostat will give you clear indication that temperatures are rising above and beyond safe levels of operation.
- If you have a forward-looking infrared (FLIR) camera handy, it’ll quickly show you when a machine reaches overload temperatures.
- Want a high-tech solution? Smart temperature sensors will do more than just tell you about an overheat — they pinpoint exactly when it happened and at what temperature.
Any of these methods will qualify an overheat, so you can be sure that’s what you’re dealing with. Once confirmed, you’ll need to understand why your electric motor keeps exceeding safe operating temperatures.

Common problems leading to overheating in motor equipment
As is the case with any electrical system, heat is a product of poor operating conditions. What happens when an electric motor overheats? Overheating is most generally traced back to one of these five core issues:
1. Electrical overload caused by excessive voltage supply or overwork by drawing more current will lead to overheating issues. As the motor works harder or under unusual load, heat will be the chief byproduct, leading to failure.
2. Low resistance is the most common reason behind electric motor failure. Degradation of motor windings by heat will pave the way for short-circuits and leakages, which leave the motor at risk for failure.
3. Contamination of dust and debris will raise the internal temperature of a motor and keep it from cooling, which leads to excessive heat over a longer period of time. This generally occurs without proper maintenance or venting for particles.
4. Start-stop frequency plays a big role in heat damage. Excessively starting, stopping, and starting your motor again won’t allow it to cool properly. The result is a high-heat environment that wears on the integrity of components.
5. Vibration from a condition like soft foot leads to excessive heat. If vibrations are severe enough, they’ll raise temperatures to unsafe levels and stress components beyond their capacity for heat.
Most electrical technicians can spot heat-causing catalysts like these upon disassembly or inspection of the motor.
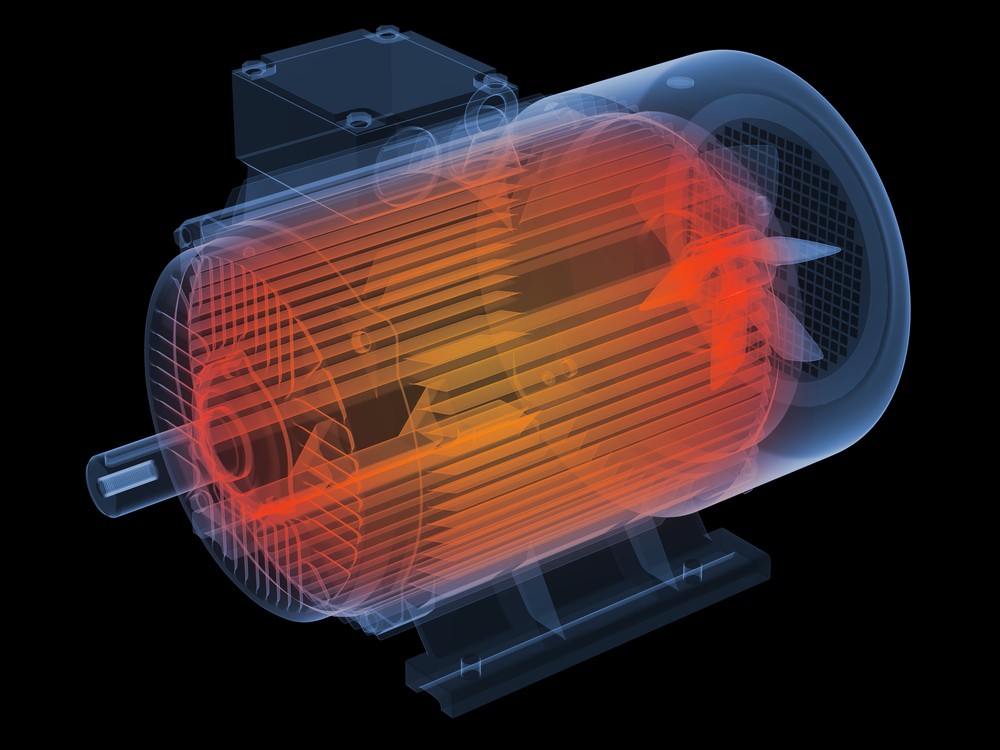
Motor overheating troubleshooting
The issue with heat-induced failures is that they’ll continue to happen until maintenance solves the core issue. Thankfully, there are ways to nip these problems in the bud without too much modification to a maintenance plan. Here are a few tips for how to fix an overheated electric motor:
- Thorough, routine maintenance ensures individual components within the electrical system get the attention they need to minimize overwork and overheating.
- Smart sensor installation can alert techs to heat-induced issues in real time, enabling fixes and modifications before total breakdown occurs.
- Installation of overload protectors and proper configuration will prevent load issues, directly addressing several catalysts for head damage.
Alongside friction in mechanical equipment, heat is the bane of any factory’s electrical devices. Keeping heat in check starts with understanding what causes it and what you can do to minimize or eliminate those variables.

