Manufacturing the Future
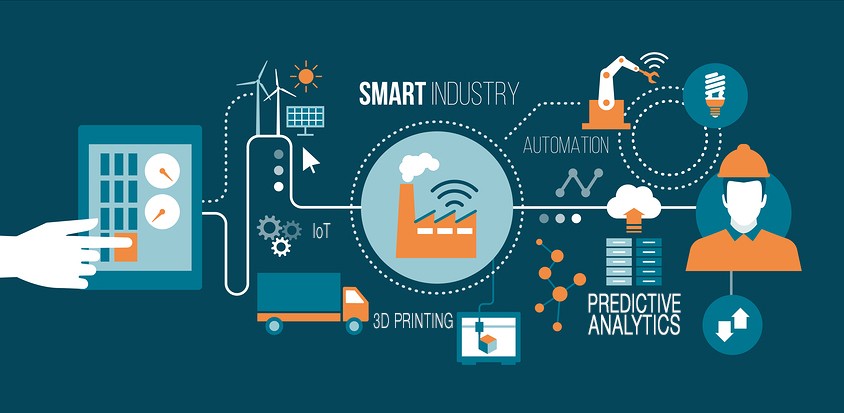
Starting in the mid-18th century, the Industrial Revolution changed the world of manufacturing forever. The use of steam engines paved the way for automation and greater productivity than anyone had ever seen. Now, in the 21st Century, we find ourselves once again in a time of exciting changes. The so-called Digital Age has brought with it the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and game-changing 3D printing.
The Internet of Things is changing manufacturing
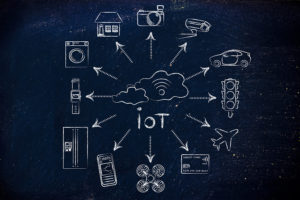 In the IoT, “things” include smart products with the power to connect, network, and communicate not only with one another but also with manufacturers, executives, and anyone else who might need to be in the loop. Essentially, the main connections that communicate to one another include: people-to-people, people-to-things, and things-to-things. The Forbes article describes a hypothetical scenario to better visualize this by explaining, “Say for example you are on your way to a meeting; your car could have access to your calendar and already know the best route to take. If the traffic is heavy your car might send a text to the other party notifying them that you will be late. What if your alarm clock wakes up you at 6 a.m. and then notifies your coffee maker to start brewing coffee for you?”
In the IoT, “things” include smart products with the power to connect, network, and communicate not only with one another but also with manufacturers, executives, and anyone else who might need to be in the loop. Essentially, the main connections that communicate to one another include: people-to-people, people-to-things, and things-to-things. The Forbes article describes a hypothetical scenario to better visualize this by explaining, “Say for example you are on your way to a meeting; your car could have access to your calendar and already know the best route to take. If the traffic is heavy your car might send a text to the other party notifying them that you will be late. What if your alarm clock wakes up you at 6 a.m. and then notifies your coffee maker to start brewing coffee for you?”
Traditionally, to prevent issues like catastrophic engine failure, airplane mechanics have performed routine aircraft inspections. Now, with the help of the IoT, engine components in danger of wearing out can alert engineers to issues who can then help prevent problems before they occur. Over time, analysts compile this information and the resulting data enables engineers to predict when parts need to be replaced.
Data science and predictive analytics
 The use of information to increase manufacturing efficiency is known as data analytics. Data mining, predictive analytics, and machine learning are three types of advanced, and commonly used, types of analytics. Each of these analyzes sets of information, then provides valuable quantitative or qualitative data. These tools significantly help business professionals make better decisions that serve multiple purposes, such as better understanding consumer behavior or preventing machine failure.
The use of information to increase manufacturing efficiency is known as data analytics. Data mining, predictive analytics, and machine learning are three types of advanced, and commonly used, types of analytics. Each of these analyzes sets of information, then provides valuable quantitative or qualitative data. These tools significantly help business professionals make better decisions that serve multiple purposes, such as better understanding consumer behavior or preventing machine failure.
For years, industrialists have puzzled over why and how their operations weren’t as productive as they’d planned. Now, through precise real-time data analysis, manufacturers can be certain which aspects of their operations are most effective — and which they can terminate. This ability could lead to an exponential increase in industrial efficacy and an exponential decrease in equipment failure rates.
3-D printing becomes mainstream
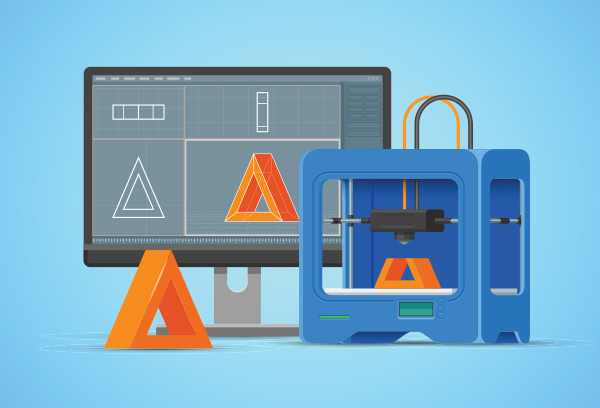 Now that the IoT and data analytics can work together to tell engineers which parts will wear out and when, the only piece of the puzzle remaining is replacement part production. This is where 3-D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is changing the game. Rather than ordering new components and waiting for them to arrive, manufacturers can program part specifications into a computer and use a 3-D printer to bring those parts to life. This not only allows for real-time delivery, it also saves you money by requiring less inventory on hand. Another perk, for manufacturing specifically, is the amount of customization ability a 3-D printer gives you — allowing you to meet specific customer needs or adjustments within your own plant more easily.
Now that the IoT and data analytics can work together to tell engineers which parts will wear out and when, the only piece of the puzzle remaining is replacement part production. This is where 3-D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is changing the game. Rather than ordering new components and waiting for them to arrive, manufacturers can program part specifications into a computer and use a 3-D printer to bring those parts to life. This not only allows for real-time delivery, it also saves you money by requiring less inventory on hand. Another perk, for manufacturing specifically, is the amount of customization ability a 3-D printer gives you — allowing you to meet specific customer needs or adjustments within your own plant more easily.
The modern world is changing faster every day, but with the trifecta of the IoT, data analytics, and 3-D printing, savvy manufacturers are sure to keep up with a great deal being thrown their way.