AC vs. DC: How To Choose the Right Drive for the Application
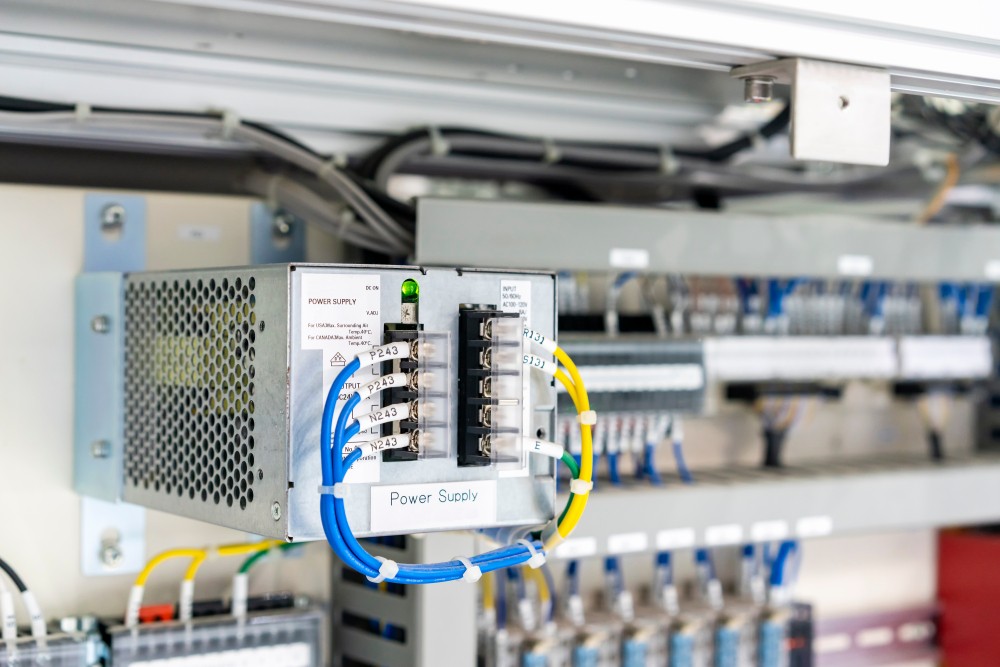

In manufacturing, electric drives are pivotal for controlling motor speed and torque, directly influencing energy efficiency and process precision. Generally speaking, equipment will have either an alternating-current (AC) or direct-current (DC) drive. The distinction between AC and DC drives involves various factors, including their operational mechanisms, advantages, and suitability for specific applications.
AC drives
AC drives are synonymous with variable-frequency drives (VFDs). They govern the operation of AC motors by altering the power’s frequency and voltage. This adjustment is crucial for tasks demanding speed variation and energy conservation. With components like inverters, AC drives not only offer precise control but also promise energy efficiency and reduced maintenance, thanks to their minimal mechanical parts.
DC drives
DC drives manage the speed of DC motors by modifying the input voltage. They provide a more straightforward control mechanism suitable for environments requiring simplicity and high starting torque. These characteristics make DC drives favorable for machinery like plastic extrusion units and printing presses, where they deliver consistency and adaptability across various speeds.

AC drives vs. DC drives
Manufacturing equipment managers are likely to encounter both AC and DC drives across the factory environment. Discerning their differences helps in understanding everything from their maintenance needs to best practices in managing them. Key comparison points include:
- Efficiency and energy consumption: AC drives excel in energy efficiency and are particularly beneficial under variable load conditions. DC drives, while efficient, are often more suited to applications requiring consistent speed and may consume more power during load fluctuations.
- Control complexity and range: AC drives offer sophisticated control features, which are essential for processes demanding precise speed variations or advanced operational commands. DC drives provide simplicity and ease of control, making them ideal for a wide range of speed requirements without the need for complex functionalities.
- Maintenance and durability: AC drives are characterized by lower maintenance needs due to their electronic components, contributing to a longer operational lifespan. DC drives demand more regular maintenance attention due to wear-prone elements like brushes, potentially shortening their effective life in comparison.
- Cost-effectiveness: DC drives may have a lower initial investment, which is attractive for budget-conscious operations. AC drives, though sometimes more expensive upfront, can prove more economical in the long run when factors like maintenance, repair, and energy usage are considered.
- Environmental impact: AC drives are generally preferred due to their lower environmental footprint and role in reducing overall energy consumption. The environmental benefits of DC drives are context-dependent, often hinging on the application and the nature of the electrical supply.
Specific drives for specific applications
Neither AC nor DC drives offer a one-size-fits-all application in the factory setting. AC drives are lauded for their energy economy and advanced controls, which are ideal for complex, variable-speed applications. DC drives, with their simplicity and excellent start-up torque, are perfect for processes requiring straightforward control and consistent performance.
The key to selecting a drive and maintaining its efficacy lies in aligning the choice of technology with the industrial application. The right drive can help ensure a balance of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability in the demanding world of factory production.